Customized Physical Therapy Can Ease Lower Back Pain
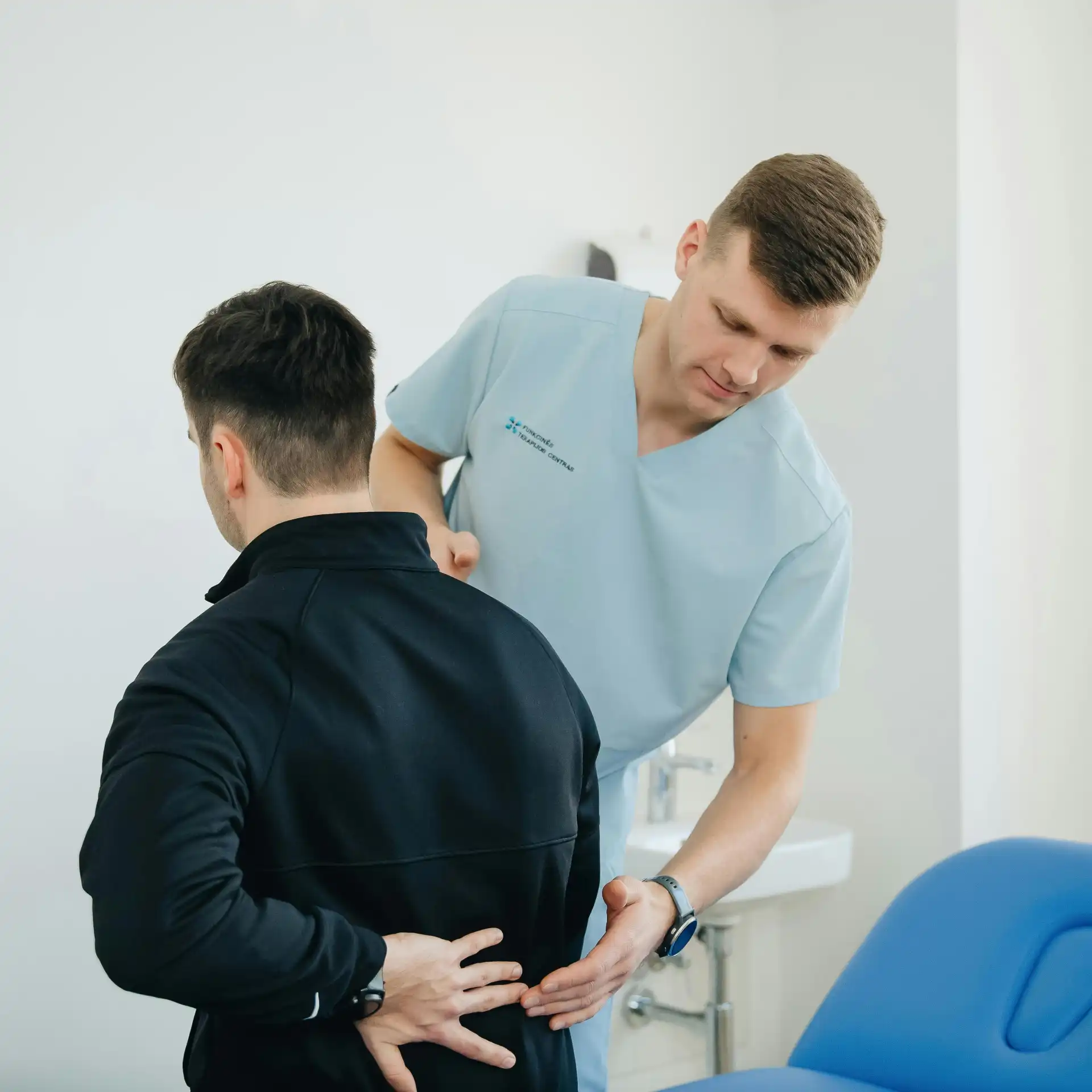
Lower back pain is a common issue that affects millions of people worldwide. Whether it’s due to poor posture, an injury, or degenerative conditions, lower back pain can significantly impact daily life. Customized physical therapy offers a targeted approach to alleviate lower back pain, providing long-term relief and improving quality of life.
1. Personalized Assessment and Treatment Plans
One of the key benefits of customized physical therapy is the personalized assessment. Physical therapists conduct thorough evaluations to identify the specific causes of lower back pain in each patient. This assessment includes examining posture, range of motion, muscle strength, and any underlying conditions. Based on these findings, they develop a tailored treatment plan that addresses the unique needs of the individual.
2. Strengthening Core Muscles
A strong core is essential for supporting the lower back. Weak or imbalanced core muscles can lead to poor posture and increased strain on the lower back. Physical therapists design exercises that target the abdominal and back muscles, helping to strengthen and stabilize the core. These exercises not only reduce pain but also prevent future episodes of lower back pain by providing better support for the spine.
3. Improving Flexibility and Mobility
Tight muscles and restricted mobility can contribute to lower back pain. Physical therapy includes stretching and mobility exercises to improve flexibility in the hips, hamstrings, and lower back. Increased flexibility helps reduce tension and pressure on the lower back, alleviating pain and enhancing overall movement.
4. Manual Therapy Techniques
Customized physical therapy often incorporates manual therapy techniques such as massage, joint mobilization, and myofascial release. These hands-on treatments help to reduce muscle tension, improve circulation, and enhance tissue health. Manual therapy can provide immediate pain relief and is an integral part of a comprehensive treatment plan.
5. Education on Proper Body Mechanics
Understanding how to move correctly is crucial for preventing and managing lower back pain. Physical therapists educate patients on proper body mechanics and posture, whether sitting, standing, or lifting objects. Learning the right techniques can prevent further strain on the lower back and promote long-term spinal health.
6. Progressive Exercise Programs
As patients progress, physical therapists adjust their exercise programs to ensure continued improvement. These progressive programs are designed to challenge the body safely, promoting strength, endurance, and flexibility. The goal is to help patients return to their normal activities without pain and with a reduced risk of recurrence.
7. Pain Management and Relief
Physical therapists use various modalities to manage and relieve pain, such as heat and cold therapy, electrical stimulation, and ultrasound. These treatments can reduce inflammation, improve blood flow, and decrease pain signals, providing immediate and lasting relief.
Customized physical therapy is an effective and holistic approach to easing lower back pain. By offering personalized assessment, targeted exercises, manual therapy, education, and progressive programs, physical therapy addresses the root causes of pain and promotes long-term healing. If you’re struggling with lower back pain, consider consulting a physical therapist to develop a customized treatment plan that fits your specific needs.